Updated: 19.01.2021
First Aid Summary
First aid: first and immediate assistance in an emergencyFirst aid kit: supplies and equipnet used to give emergency medical treatment
Bleeding: blood escaping the body
External bleeding: blood leaving the body through a wound
Internal bleeding: blood collecting inside the body
Arterial bleeding: from an artery, the blood is bright and flows quicky
Venous bleeding: from a vein, the blood id dark and flows slowly
Asphyxiation: not breathing properly, defficient suppy of oxygen causes hypoxia
Choking: object stuck in the throat or windpipe, blocks the air from flowing
Strangling: compression of the neck, closure of the airways and arteries
CPR: cardiopulmonary resuscitation to manually preserve intact brain function
30 chest compressions to 2 rescue breaths
Bone fracture: an X-ray necessary, treatment should involve immobilization, a splint can by applied to a broken limb, the wound shoud be cleaned and protected by sterile dressing
 First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person suffering from illnes or injury. Its aim is to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening and to promote recovery. An emergency usually involves loss of consciousness, heavy blood loss, suspected broken bones, chest pain lasting more than 15 minutes, difficulty breathing, overdose or poisoning. A first aid kit is a collection of supplies and equipment used to give medical treatment.
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person suffering from illnes or injury. Its aim is to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening and to promote recovery. An emergency usually involves loss of consciousness, heavy blood loss, suspected broken bones, chest pain lasting more than 15 minutes, difficulty breathing, overdose or poisoning. A first aid kit is a collection of supplies and equipment used to give medical treatment.
The primary goals of first aid are the 5P's, preserve life, reduce the level of pain, prevent further harm, promote recovery and protect the unconscious.
Bleeding, also called hemorrhage, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels.
External bleeding is when blood is leaving the body through a wound. Internal bleeding is a loss of blood that collects inside the body. The symptoms include coughing up or vomiting blood, faintness or dizziness, weak pulse and pale skin. This medical emergency should be treated immediately by medical professionals, the first aid giver should call to the emergency medical services, lay the patient down and check vital functions.
Venous bleeding occurs when a vein is damaged, the blood is dark red and leaks slowly and steadily from the wound. First aid includes applying pressure and dressing, if a limb is wounded, lifting up the limb can also help.
Arterial bleeding occurs when an artery is damaged, the blood is bright red to yellowish, sprays out of the wound and the patient is usually pale. First aid includes applying pressure and dressing, if a limb is wounded, lifting up the limb can also help. A tourniquet can also by used to slow the bleeding.
Asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen that arises from abnormal breathing. It causes generalized hypoxia, a pathological state of insufficient supply of oxygen.
This can happen for example by choking, when an object becomes stuck in the throat or the windpipe and blocks air from flowing into the lungs. Symptoms include inability to speak, difficulty in breathing, violent coughing, clutching the throat, attempting to induce vomiting, change of colour in the face and unconsciousness. The basic treatment involves hard back slaps and then Heimlich maneuver. If the person loses consciousness, CPR is recommended.
Drowning is defined as respiratory impairment as a result of being in a liquid, usually water. Symptoms following rescue may include breathing problems, vomiting, confusion and unconsciousness. Treatment should include opening the airway and performing CPR if the heart is not beating.
Strangling is compression of the neck, it typically occurs in cases of violence and accidents. It can induce one or more conditions, some leading to death, including closure of arteries and veins and closure of the airway. The constriction from the neck should be immediately removed, while the body is supported. The patient should be moved as little as possible, in case of spinal injury. The patient should be laid down, the airway opened and CPR performed if necessary.
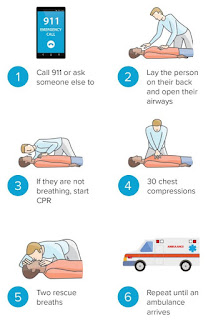
STEP 1: shake and stout
STEP 2: check breathing and bleeding
STEP 3: call emergency services
STEP 4: give 30 chest compressions
STEP 5: give 2 rescue breaths
STEP 6: repeat until help arrives
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or health. These emergencies require assistance dependent of the severity of the condition.
Anaphylaxis, a serious allergic reaction, occurs rarely with stings and insect bites. Symptoms include swelling, breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, vomiting, low blood pressure and a rash. Swelling can be life-threatening and urgent medical attention is required. Carrying an epinephrine autoinjection and identification regarding the condition is recommended in people with a history of this condition.
A bone fracture is a condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the bone, severe cases include bone broken into several pieces. Symptoms include pain, deformity, swelling and bruising, loss of function, inability to move, and in open fractures, bone protruding from the skin. Treatment should involve immobilization, a splint can by applied to a broken limb, the wound shoud be cleaned and protected by sterile dressing. Later treatment can involve surgical corrections.
A burn is a type of injury to tissues caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction or radiation. Treatment depends on the severity of the burn, major burns require prolonged treatment in specialized burn centres. Cooling with water may help pain and decrease damage, a sterile bandage can be applied. Clothing stuck to the skin should not be removed and ice and creams should not be applied. Scalding is a form of thermal burn resulting from heated fluids. Most scalds are considered first or second degree burns, but prolonged contact can cause more damage.
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, often caused by sudden trauma. It can cause damage to the ligaments, tendons, muscles and nerves, symptoms include pain, joint instability and deformity, bruising, stiffness and difficulty moving. Reduction should be performed only by trained professionals, an untrained person can substantially worsen the injury. It is important that the joint is x-rayed and reduced as soon as possible and they are usually held in place by a splint or bandage.
CPR: cardiopulmonary resuscitation to manually preserve intact brain function
30 chest compressions to 2 rescue breaths
Bone fracture: an X-ray necessary, treatment should involve immobilization, a splint can by applied to a broken limb, the wound shoud be cleaned and protected by sterile dressing
 First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person suffering from illnes or injury. Its aim is to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening and to promote recovery. An emergency usually involves loss of consciousness, heavy blood loss, suspected broken bones, chest pain lasting more than 15 minutes, difficulty breathing, overdose or poisoning. A first aid kit is a collection of supplies and equipment used to give medical treatment.
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person suffering from illnes or injury. Its aim is to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening and to promote recovery. An emergency usually involves loss of consciousness, heavy blood loss, suspected broken bones, chest pain lasting more than 15 minutes, difficulty breathing, overdose or poisoning. A first aid kit is a collection of supplies and equipment used to give medical treatment.The primary goals of first aid are the 5P's, preserve life, reduce the level of pain, prevent further harm, promote recovery and protect the unconscious.
Bleeding, also called hemorrhage, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels.
External bleeding is when blood is leaving the body through a wound. Internal bleeding is a loss of blood that collects inside the body. The symptoms include coughing up or vomiting blood, faintness or dizziness, weak pulse and pale skin. This medical emergency should be treated immediately by medical professionals, the first aid giver should call to the emergency medical services, lay the patient down and check vital functions.
Venous bleeding occurs when a vein is damaged, the blood is dark red and leaks slowly and steadily from the wound. First aid includes applying pressure and dressing, if a limb is wounded, lifting up the limb can also help.
Arterial bleeding occurs when an artery is damaged, the blood is bright red to yellowish, sprays out of the wound and the patient is usually pale. First aid includes applying pressure and dressing, if a limb is wounded, lifting up the limb can also help. A tourniquet can also by used to slow the bleeding.
Asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen that arises from abnormal breathing. It causes generalized hypoxia, a pathological state of insufficient supply of oxygen.
This can happen for example by choking, when an object becomes stuck in the throat or the windpipe and blocks air from flowing into the lungs. Symptoms include inability to speak, difficulty in breathing, violent coughing, clutching the throat, attempting to induce vomiting, change of colour in the face and unconsciousness. The basic treatment involves hard back slaps and then Heimlich maneuver. If the person loses consciousness, CPR is recommended.
Drowning is defined as respiratory impairment as a result of being in a liquid, usually water. Symptoms following rescue may include breathing problems, vomiting, confusion and unconsciousness. Treatment should include opening the airway and performing CPR if the heart is not beating.
Strangling is compression of the neck, it typically occurs in cases of violence and accidents. It can induce one or more conditions, some leading to death, including closure of arteries and veins and closure of the airway. The constriction from the neck should be immediately removed, while the body is supported. The patient should be moved as little as possible, in case of spinal injury. The patient should be laid down, the airway opened and CPR performed if necessary.
How to Perform CPR
CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) is an emergency procedure that combines chest compressions often with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It involves chest compressions for adults 5-6cm deep and at a rate of 100-120 per minute, set to breathing ratios at 30 to 2. It alone is unlikely to restart the heart, its main purpose is to delay tissue damage and death, especially brain damage. An untrained person may deliver hands-only CPR.STEP 1: shake and stout
STEP 2: check breathing and bleeding
STEP 3: call emergency services
STEP 4: give 30 chest compressions
STEP 5: give 2 rescue breaths
STEP 6: repeat until help arrives
Other Conditions
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or health. These emergencies require assistance dependent of the severity of the condition.
Anaphylaxis, a serious allergic reaction, occurs rarely with stings and insect bites. Symptoms include swelling, breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, vomiting, low blood pressure and a rash. Swelling can be life-threatening and urgent medical attention is required. Carrying an epinephrine autoinjection and identification regarding the condition is recommended in people with a history of this condition.
A bone fracture is a condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the bone, severe cases include bone broken into several pieces. Symptoms include pain, deformity, swelling and bruising, loss of function, inability to move, and in open fractures, bone protruding from the skin. Treatment should involve immobilization, a splint can by applied to a broken limb, the wound shoud be cleaned and protected by sterile dressing. Later treatment can involve surgical corrections.
A burn is a type of injury to tissues caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction or radiation. Treatment depends on the severity of the burn, major burns require prolonged treatment in specialized burn centres. Cooling with water may help pain and decrease damage, a sterile bandage can be applied. Clothing stuck to the skin should not be removed and ice and creams should not be applied. Scalding is a form of thermal burn resulting from heated fluids. Most scalds are considered first or second degree burns, but prolonged contact can cause more damage.
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, often caused by sudden trauma. It can cause damage to the ligaments, tendons, muscles and nerves, symptoms include pain, joint instability and deformity, bruising, stiffness and difficulty moving. Reduction should be performed only by trained professionals, an untrained person can substantially worsen the injury. It is important that the joint is x-rayed and reduced as soon as possible and they are usually held in place by a splint or bandage.


